Verichains Weekly Security Digest | August 2023 Week 3
Verichains Weekly Security Digest | August 2023 Week 3
In this week's Security Digest, Verichains Research Team presented our critical 0-day attacks on MPC vaults and wallets at the premier cybersecurity conference, Black Hat USA 2023.
In incident news, the DeFi market suffered a $1,386,000 loss with Steadfi leading the chart for over $1,000,000 in lost funds. Meanwhile, reentrancy vulnerabilities continue to run rampant week after week.
Verichains x Black Hat USA 2023
On Thursday, August 10th, Verichains Research Team presented our groundbreaking research project and the discovery of multiple private key extraction zero-day attacks in popular Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) libraries called TSSHOCK at Black Hat USA 2023, the premier cybersecurity conference.
The conclusion of our 10 months journey in open-source vulnerability research and responsible disclosure through our security advisory of the attacks starting in October 2022. Since it was first announced to the public back in March 2023, Verichains had completed responsible disclosure to affected vendors verified through their open-source TSS implementation. Additionally, we've received inquiries from a number of private implementation vendors, and we have privately shared our research with these vendors under strict NDA.
To understand the severity of TSSHOCK, we can refer to THORChain's immediate reaction upon receiving our disclosure complete with a working PoC exploit on testnet that completely breaks their MPC vault and could steal $180 million (in TVL), THORChain immediately suspended their mainnet globally for 24 hours.

TSSHOCK is effective at a foundational layer of threshold ECDSA, implicating the potential list of vulnerable vendors to be greater than, and beyond the scope of our survey. Read more on our complete technical analysis, including recommendations here: https://www.verichains.io/tsshock/
Through the disclosure of TSSHOCK, Verichains urges projects and vendors to implement appropriate remediation and highlights the importance of thorough audits, rigorous evaluations, and continuous improvement in security measures.
Last Week’s Incidents
🚨Project: Steadefi
⛓️Chain: Ethereum
💥Type: Compromised Wallet
💸Loss amount: $1,100,000
Last week a DeFi project called Steadefi was attacked for $1,100,000 as its deployer wallet was compromised. The incident revolves around a vulnerability in the project’s protocol's deployer wallet that governs ownership of all vaults within the system. The attacker successfully compromised this deployer wallet, thereby assuming control over both lending and strategy vaults. Subsequently, they then executed actions normally reserved for the owner, including granting borrowing privileges to any wallet from the lending vaults. As a direct consequence, the attacker managed to exhaust the lending capacity on both the Arbitrum and Avalanche networks, converting the acquired assets to Ethereum through strategic swaps and bridges.
Notably, the depositor vaults remained unaffected due to the absence of mechanisms enabling the exploiter to withdraw from them. While withdrawal from strategy vaults remains potentially viable for users, it hinges on the attacker's restraint from pausing these vaults. Furthermore, the attacker's decision to halt the farms contract operation restricts users, as well as the attacker, from withdrawing svTokens or ibTokens associated with the farms.
At the time of writing, the project failed to contact the attacker but has successfully recovered 50% of the lost fund and is carrying out a reimbursement program.
🚨Project: Earning Farm
⛓️Chain: Ethereum
💥Type: Reentrancy Attack
💸Loss amount: ~$286,000
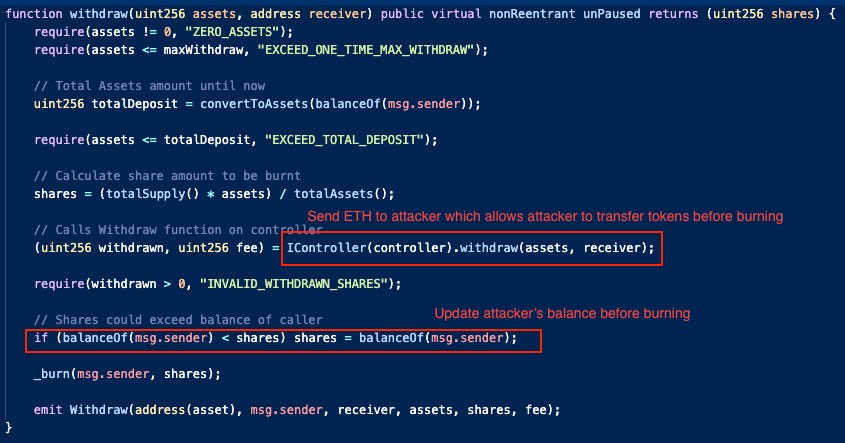
In another reentrancy attack, a project called Earning Farm was attacked for around ~$286,000. The root cause of the attack was attributed to a flaw within the withdrawal logic embedded in the ‘controller’ contract. When users perform a withdrawal, the contract would dispatch ETH to the user prior to conducting an assessment of the sufficiency of the user’s balance. Exploiting this vulnerability, the attacker relocates tokens to an alternate address prior to initiating the asset-burning process.